
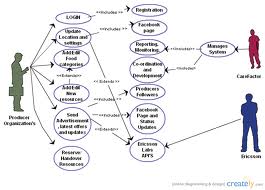

This is indicated using a dashed line connecting the two use cases with an arrow pointing toward the second use case.

Include associations: This type of association means that a base use case includes a second use case.

An arrow is also used to indicate the dependency between the two use cases. Since there are two different types of associations that can exist between use cases, the lines are expanded upon using a keyword referred to as a stereotype in UML which is enclosed in double chevrons. Dashed lines are used for relationships between different use cases. A solid line between an actor and a use case indicates that the actor and the use case described in the oval are related. The relationships between these elements are described using lines to link them. Other UML diagram types are used for this purpose, such as activity diagrams used to chronologically depict workflows and sequence diagrams used to show the exchange of messages between different elements in a system. In comparison to other behavioral diagrams in UML, the use case diagram is quite static as it can only be used to describe the action and goal but not the exact sequence of the various workflows and actions. The use case diagram is a special case within this group, since it depicts what behavior is expected from a system or software program in a specific use case. Instead, they show the planned or actual flow of processes that can be expected when using the program or software. In contrast, behavioral diagrams do not focus on static structures. A common example of this is the class diagram which can be used to group elements and visualize hierarchies. Structural diagrams focus on depicting all elements in a system and their relationship to each other. They can be divided into categories: structural diagrams, behavioral diagrams, and interaction diagrams with interaction diagrams being a subset of behavioral diagrams. Since it would be too complicated and confusing to depict all objects, relationships and processes in a single diagram, UML uses 14 different types of diagrams.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
